Simple Flask API Server For Beginners - With Sample Code
Open-source API server that might help beginners to understand better the API concept
Hello Coders!
This article presents a simple API starter that might help beginners to understand better the API concept. The codebase can be downloaded from Github and used for eLearning activities or production. The framework that powers the API is Flask, a leading software library actively supported and versioned by many open-source enthusiasts.
Thanks for reading!What's in the box:
- 👉 Simple API over a minimal
Datastable - 👉
SQLite Persistencemanaged by an elegant ORM (SqlAlchemy) - 👉
Powerful APIcore provided by Flask-RestX - 👉
Strong Input validation - 🎁 Free support via email and Discord (1k+ community).
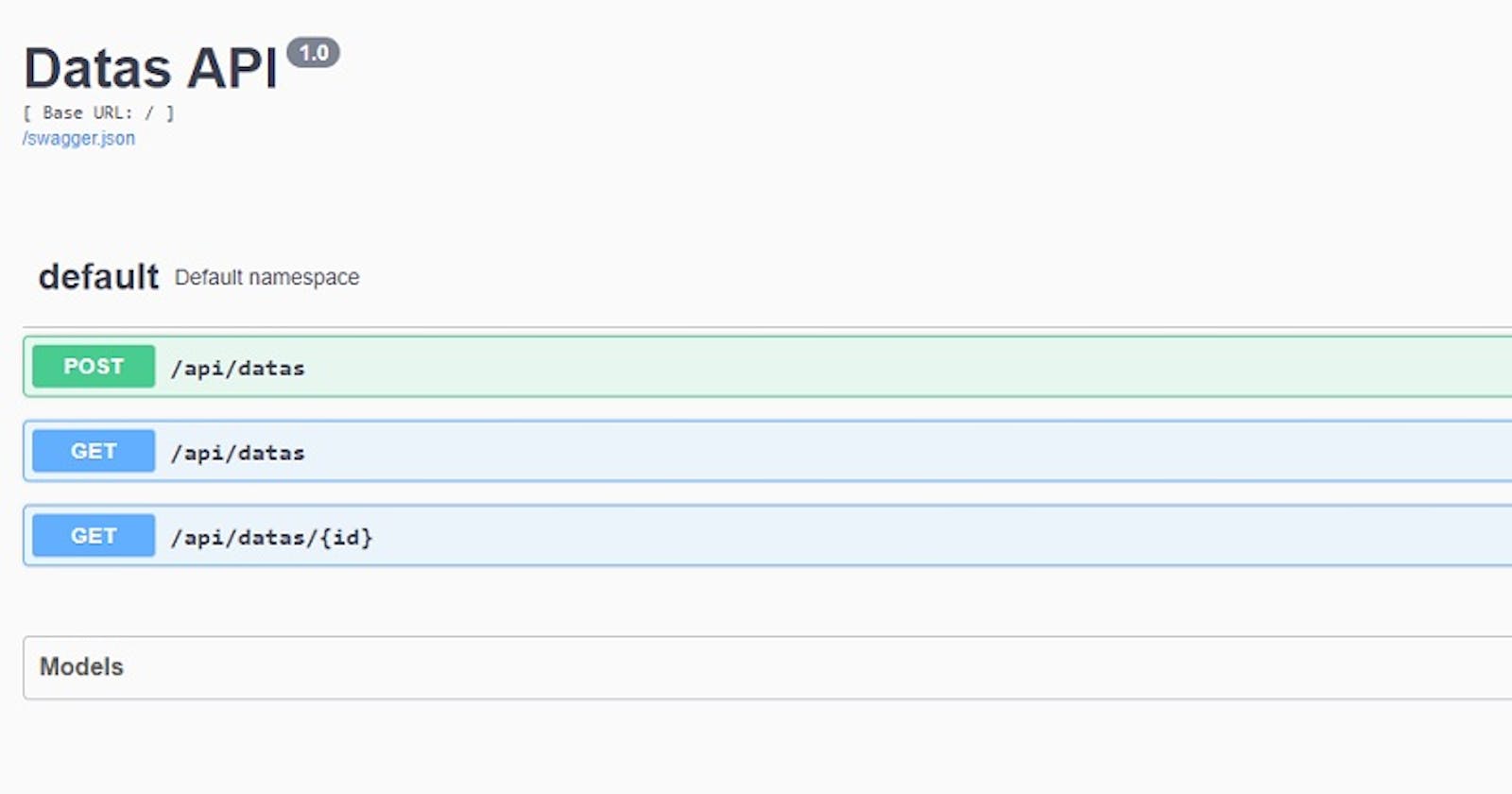
API Definition
| Route | Verb | Info | Status |
/datas | GET | return all items | ✔️ |
| POST | create a new item | ✔️ | |
/datas:id | GET | return one item | ✔️ |
| PUT | update item | ✔️ | |
| DELETE | delete item | ✔️ |
Technology Stack
Flaskfor routing and overall managementFlask-RestXfor APIFlask-SqlAlchemy- manages the DB with minimal codeDockerset up provides a quick start for lazy devs (like me)
✨ API Coding & Implementation Rules
- Simple Interface
- Consistent, intuitive actions
- Use the right verbs for each action
GETforread-onlyactionsDELETEfor item removalPOSTfor updates
- Strong Input Validation
✨ Codebase Structure
All relevant files are listed below. Other files like docker-compose.yml, README, LICENSE are omitted.
api-server-flask/
├── api
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── config.py
│ ├── models.py
│ └── routes.py
├── README.md
├── requirements.txt
└── run.py
A few words about each one:
run.py- the entry pointapi folder__init__.pyconstructs the APPmodels.py- define a single (simple) modelroutes.py- does the hard workconfig.py- implements a minimal set up
✨ API Models
The information managed by the API is saved using a simple table defined with three fields: id, data, date_created. Here is the source code:
# Contents of "api/models.py" (truncated)
...
class Datas(db.Model):
id = db.Column(db.Integer() , primary_key=True)
data = db.Column(db.String(256) , nullable=False)
date_created = db.Column(db.DateTime() , default=datetime.utcnow)
...
The source code provides a few helpers that make our life, as a developer, easier:
update_data- update thedatafieldsave- save & commit the updates of the current objecttoJSON- returns the JSON representation
✨ Routing
Each method is kept as simple as possible but at the same time, provides a robust validation and elegant SQL access.
For instance, the route that manages the update operation for an item:
# Contents of "api/routes.py" (truncated)
....
@rest_api.route('/api/datas/<int:id>')
class ItemManager(Resource):
...
"""
Update Item
"""
@rest_api.expect(update_model, validate=True)
def put(self, id):
item = Datas.get_by_id(id)
# Read ALL input from body
req_data = request.get_json()
# Get the information
item_data = req_data.get("data")
if not item:
return {"success": False,
"msg": "Item not found."}, 400
item.update_data(item_data)
item.save()
return {"success" : True,
"msg" : "Item [" +str(id)+ "] successfully updated",
"data" : item.toJSON()}, 200
...
Let's iterate over the relevant lines:
@rest_api.route('/api/datas/<int:id>')defines the route
Flask will route the request to this section when user access /api/datas/1 for instance .
@rest_api.expect(update_model, validate=True)
This decorator trigger a validation previously defined as bellow:
update_model = rest_api.model('UpdateModel', {"data": fields.String(required=True, min_length=1, max_length=255)})
If the data field has a size over 255, the request is rejected. For us, as developers, the coding effort is minimal.
The next steps performed by our handler are:
- Select the Item from DB using the
IDitem = Datas.get_by_id(id)via SQLAlchemy
- Exit with a comprehensive error if item not found
- If Item is found
- Update the
datafield - Save the new object in database
- Update the
✨ Where to go from here
This simple API will be extended with more features soon:
- Add more fields to
Datasmodel - Implement authentication
- restrict
updateactions to authenticated users.
Have an idea? Please mention your suggestion in the comments section.
Thank you!
✨ For more resources, feel free to access:
- 👉 Flask - the official website
- 👉 Flask-RestX - library docs
- 👉 More Flask Starters to play with